New Dynamics in the Russia-Ukraine War
As the Russia-Ukraine war enters its third year, the conflict has evolved into a complex and brutal standoff with global consequences. Both Russia and Ukraine have been locked in heavy fighting across eastern and southern frontlines, where the war has taken on the nature of entrenched warfare. Key regions include the Donetsk and Luhansk areas in eastern Ukraine, as well as sections of the Zaporizhzhia and Kherson oblasts. Here, each side is pushing for small yet crucial territorial gains, and much of the fighting has centered on control of key supply routes and strategic towns.
Ukraine’s Counteroffensive and Strategic Goals
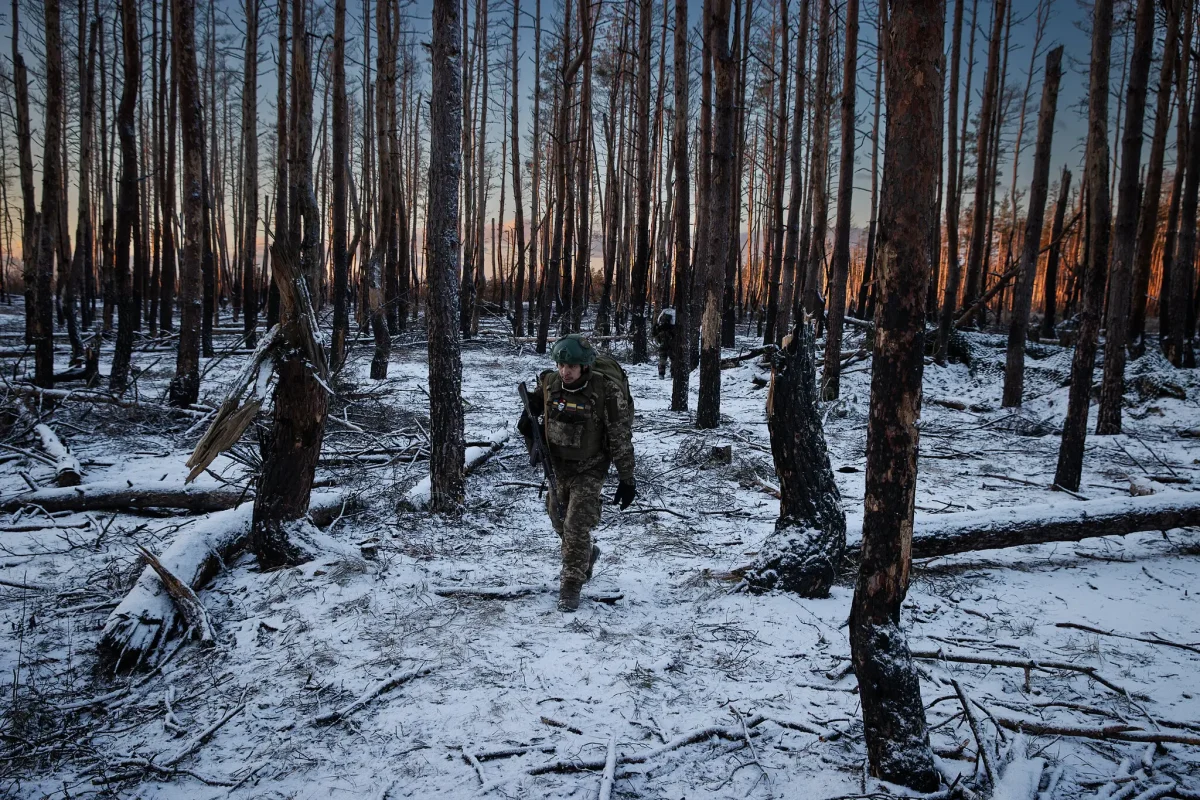
Throughout 2024, Ukraine launched a concentrated counteroffensive aiming to regain control over the southern corridor toward the Crimean Peninsula. Ukraine’s forces have specifically focused on breaking through Russian defenses near Melitopol and Berdyansk, which are crucial for both military and symbolic reasons. If successful, this push could sever Russia’s land bridge to Crimea, a vital supply route that enables Moscow to maintain control over the occupied peninsula. However, these advances have come at a steep cost, with Ukrainian troops facing fortified Russian lines, dense minefields, and significant artillery fire. Progress has been incremental, and while Ukraine’s forces have made inroads, the advances have not yet been decisive.
Russia’s Defensive Strategies and Escalation Tactics
On the Russian side, President Vladimir Putin’s government has responded by fortifying its positions in occupied territories and conducting heavy shelling and missile attacks on Ukrainian-held areas. Russia has also increased its recruitment and mobilization efforts, incorporating new troops, especially in regions where it has traditionally drawn less scrutiny, such as rural areas of Siberia. Recently, Moscow has ramped up efforts to strike at Ukraine’s critical infrastructure, particularly power and water facilities, with the intent of undermining Ukraine’s morale and pressuring its government. This tactic of targeting infrastructure is not new, but its continuation highlights Russia’s strategy of wearing down Ukrainian resistance by creating hardship during the winter months.
Western Support and Shifting Dynamics
Western support remains essential for Ukraine’s resistance, though sustaining it has become a topic of debate. The United States, European Union, and NATO members have provided extensive support in the form of financial aid, training, and sophisticated weaponry. In recent months, Ukraine has received additional air defense systems to counter Russia’s long-range missile strikes, as well as armored vehicles, drones, and artillery systems to support its counteroffensive.
However, the protracted nature of the war has raised concerns in several Western countries about the sustainability of this level of support. In the U.S., for example, political divisions over aid to Ukraine have grown more pronounced, with some lawmakers questioning the financial and strategic costs of continued involvement. European countries, too, are weighing the impacts of sanctions on their own economies, particularly regarding energy supplies. Despite these challenges, NATO remains committed to Ukraine’s defense, and discussions continue on expanding the alliance’s footprint in Eastern Europe.
Humanitarian Impact and Civilian Resilience
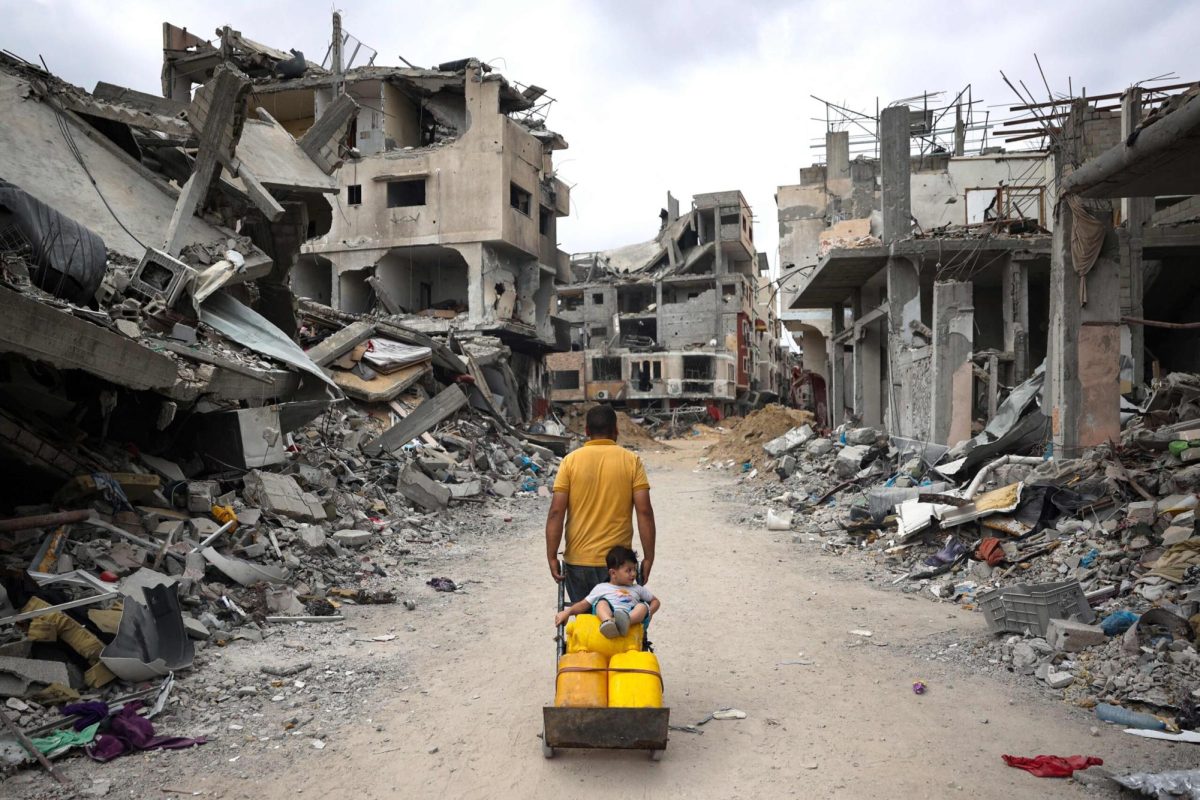
For the Ukrainian population, the war has imposed devastating hardships, with millions displaced and countless communities transformed into conflict zones. Major urban centers like Kyiv, Kharkiv, and Lviv have endured periodic missile strikes and air raids that disrupt daily life and place immense strain on public services. Humanitarian organizations are stretched thin, as civilians face shortages of food, medical supplies, and reliable access to power, especially as winter approaches. Ukraine has, however, demonstrated remarkable resilience, with volunteers and community organizations stepping up to provide aid, support reconstruction efforts, and maintain morale.
Diplomacy and Geopolitical Implications
Diplomatic efforts to resolve the conflict have thus far yielded little progress. Peace talks, facilitated by countries including Turkey, China, and members of the European Union, have failed to bring Russia and Ukraine to any lasting agreement. Moscow demands international recognition of its annexation of certain Ukrainian territories, a stance Kyiv and its Western allies categorically reject, as Ukraine remains committed to reclaiming its full territory.
Beyond Europe, the war has profound global implications. The economic fallout is especially felt in the energy and food sectors. Russia’s role as a major energy supplier has put pressure on European nations to diversify their energy sources, leading to accelerated investments in renewables and liquefied natural gas imports. Additionally, Ukraine’s significant grain exports have been disrupted, impacting food security worldwide, particularly in parts of Africa and the Middle East. The conflict has also strained relationships in the international arena, as countries like China, India, and other non-aligned nations navigate a fine line between neutrality and their strategic interests.
Looking Forward
With both sides preparing for continued offensives and no clear diplomatic resolution in sight, the Russia-Ukraine war is likely to remain an enduring conflict. Analysts suggest that the coming months may bring more intense fighting and possibly further escalation, especially if the situation reaches a tipping point in any of the contested areas. The outcome remains uncertain, but the war’s duration, its impact on global politics, and the suffering it inflicts on civilians underscore the profound and far-reaching consequences of this conflict.